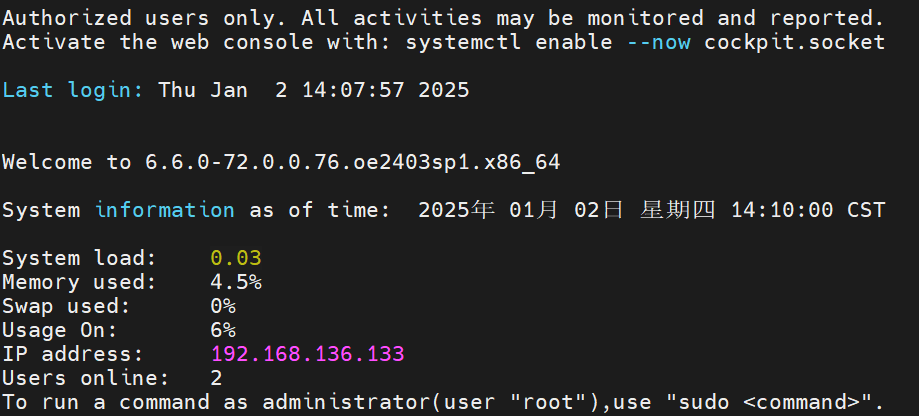
在使用 ssh 登录 Linux 时发现会输出系统的统计信息,如:
其中的第一行是在 /etc/motd 文件中定义的,这个文件会在用户登录成功后显示;第二行是在 /etc/motd.d/cockpit 文件中,这是 Cockpit Web 控制台的提示信息;之后的信息都是动态生成的,生成的脚本在 /etc/profile.d/system-info.sh,一些发行版会包含这个文件,内容如下:
#/bin/bash
#Copyright (c) [2019] Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
#generic-release is licensed under the Mulan PSL v2.
#You can use this software according to the terms and conditions of the Mulan PSL v2.
#You may obtain a copy of Mulan PSL v2 at:
# http://license.coscl.org.cn/MulanPSL2
#THIS SOFTWARE IS PROVIDED ON AN "AS IS" BASIS, WITHOUT WARRANTIES OF ANY KIND, EITHER EXPRESS OR
#IMPLIED, INCLUDING BUT NOT LIMITED TO NON-INFRINGEMENT, MERCHANTABILITY OR FIT FOR A PARTICULAR
#PURPOSE.
#See the Mulan PSL v2 for more details.
# Welcome
welcome=$(uname -r)
# Memory
memory_total=$(free -m | awk 'NR==2 { printf($2)}')
if [ $memory_total -gt 0 ]
then
memory_usage=$(free -m | awk 'NR==2 { printf("%3.1f%%", $3/$2*100)}')
else
memory_usage=0.0%
fi
# Swap memory
swap_total=$(free -m | awk 'NR==3 { printf($2)}')
if [ $swap_total -gt 0 ]
then
swap_mem=$(free -m | awk 'NR==3 { printf("%3.1f%%", $3/$2*100)}')
else
swap_mem=0.0%
fi
# Usage
usageof=$(df -h / | awk '/\// {print $(NF-1)}')
# System load
load_average=$(awk '{print $1}' /proc/loadavg)
# WHO I AM
whoiam=$(whoami)
# Time
time_cur=$(date)
# Processes
processes=$(ps aux | wc -l)
# Users
user_num=$(users | wc -w)
# Ip address
ip_pre=""
if [ -x "/sbin/ip" ]
then
ip_pre=$(/sbin/ip a | grep inet | grep -v "127.0.0.1" | grep -v inet6 | awk '{print $2}')
fi
echo -e "\n"
echo -e "Welcome to $welcome\n"
echo -e "System information as of time: \t\t$time_cur\n"
echo -e "System load: \t\t\033[0;33;40m$load_average\033[0m"
echo -e "Processes: \t\t$processes"
echo -e "Memory used: \t\t$memory_usage"
echo -e "Swap used: \t\t$swap_mem"
echo -e "Usage On: \t\t$usageof"
for line in $ip_pre
do
ip_address=${line%/*}
echo -e "IP address: \t\t$ip_address"
done
echo -e "Users online: \t\t$user_num"
if [ "$whoiam" == "root" ]
then
echo -e "\n"
else
echo -e "To run a command as administrator(user \"root\"),use \"sudo <command>\"."
fi
那么为什么这个脚本会执行呢,它在 /etc/profile 文件中被调用,它遍历了 /etc/profile.d 文件夹下的所有 shell 脚本,并检测文件是否可读:
for i in /etc/profile.d/*.sh /etc/profile.d/sh.local ; do
if [ -r "$i" ]; then
if [ "${-#*i}" != "$-" ]; then
. "$i"
else
. "$i" >/dev/null
fi
fi
done
在用户登录时,系统会自动执行 /etc/profile 文件,这个文件包含全局的 shell 设置,适用于所有用户。
留言